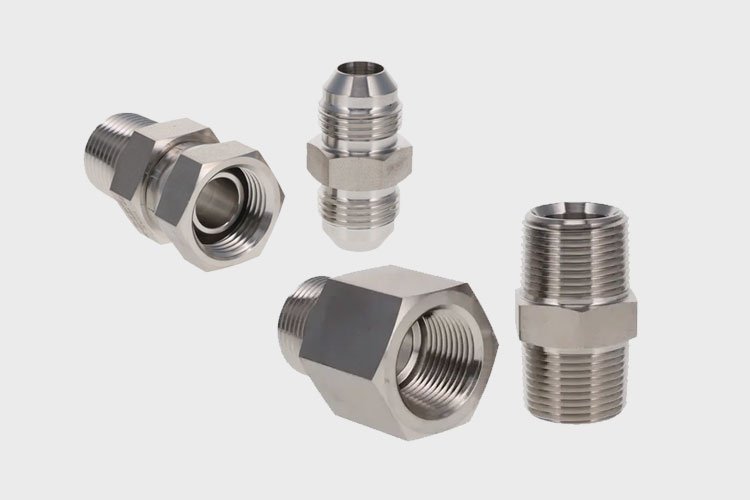
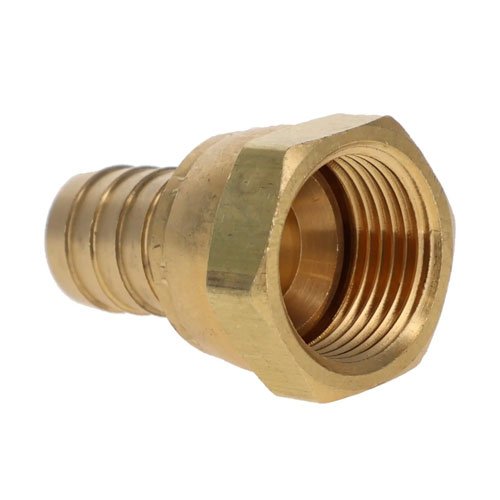
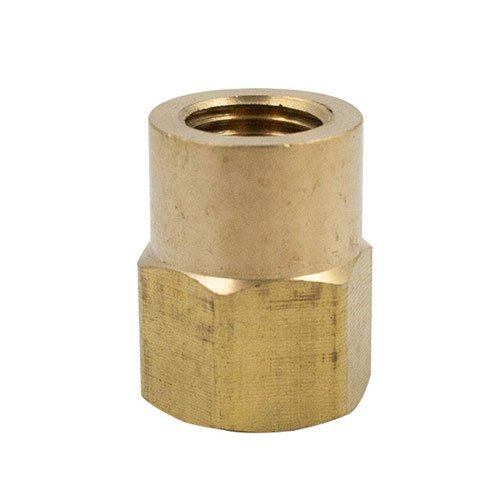
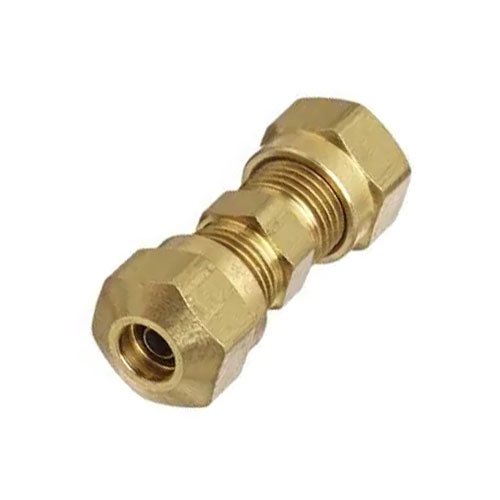
Hydraulic fittings play a crucial role in connecting hoses, tubes, and pipes within a hydraulic system. They create strong, leak-proof joints that allow smooth fluid transfer, keeping machinery safe and efficient. Without reliable fittings, even advanced hydraulic systems would lose performance and face frequent failures.
Different types of hydraulic fittings serve specific applications. For instance, threaded fittings use screw threads to secure directly into ports or connectors. Flared fittings, on the other hand, work with tubing and create a tight seal by matching a cone-shaped flare with a corresponding cone on the fitting body. Crimp fittings are often used with hoses; a crimping tool presses a ferrule around the hose to lock the connection in place. Meanwhile, push-to-connect fittings allow quick assembly without tools, as built-in O-rings or gripping parts form a firm seal.
Material selection also affects how well hydraulic fittings perform. Manufacturers often use steel, stainless steel, brass, or aluminum. Each option offers unique advantages, such as strength, resistance to corrosion, or compatibility with hydraulic fluids. In addition, sealing methods vary. Some fittings rely on threads combined with O-rings or sealants, while others use compression or mechanical grip to achieve a leak-free joint.
Hydraulic fittings support a wide range of industries. In construction, they keep excavators, loaders, and other heavy equipment running smoothly. In agriculture, they power tractors and harvesters. They also play a role in automotive systems, manufacturing plants, and industrial presses. To guarantee consistent results, many fittings follow international standards such as SAE or ISO.
Types of Hydraulic Fittings

Hydraulic Adapters
Hydraulic adapters play a key role in the hydraulic fittings and piping industries by ensuring secure and efficient connections between various components. These adapters allow for the seamless integration of pipes, hoses, and valves, often accommodating different thread types, sizes, and materials. This flexibility ensures compatibility across a range of hydraulic systems, preventing leaks and ensuring optimal pressure flow. By enabling the customization of connections, hydraulic adapters help improve system performance, durability, and safety. Hydraulic adapter’s ability to connect components while withstanding high pressures and harsh environments makes them indispensable in modern hydraulic applications.
Compression Tube Fittings
Compression fittings, comprising nuts, ferrules, and joints, are widely utilized to connect hydraulic hoses and components of various sizes, ensuring a leak-proof seal. Depending on the requirements, either one-piece or two-piece ferrule fittings with one or two ferrules (olives) can be used. These fittings play a crucial role in any hydraulic system. Because they don’t require extra sealants or gaskets and are simple to disassemble, they are ideal for applications in air conditioning, braking systems, and refrigeration.


Hydraulic Hose Fitting
Hydraulic hose fittings are essential components used to connect hydraulic hoses and other equipment in various systems. These fittings create a secure, leak-proof seal between hoses, tubes, and valves, ensuring optimal fluid flow and preventing system failures. Made from durable materials like steel or stainless steel, hydraulic hose fittings come in different types, including compression fittings, threaded, and flanged options. They are widely used in industries like construction, agriculture, automotive, and manufacturing. These fittings are crucial for maintaining the integrity of hydraulic systems, providing efficiency, and ensuring safety under high-pressure conditions.
Hydraulic Bulkhead Fittings
Hydraulic bulkhead fittings are important components in fluid systems, allowing secure connections between hoses, pipes, or tubes while maintaining system integrity. These fittings come in various types to suit different needs, including straight-through, 90-degree, and 45-degree angles, ensuring flexibility in installation. Bulkhead fittings are designed to minimize leaks and pressure loss, providing a durable solution for high-pressure applications. Common materials include stainless steel, brass, and carbon steel, offering corrosion resistance and strength. They are widely used in industries like aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing, where reliability and efficiency in fluid transfer are critical.


Hydraulic Swivel Fittings
Hydraulic swivel fittings are designed to allow rotation and flexibility in fluid systems while maintaining a secure connection. Key types include the Swivel Female x Male Adaptor, which enables easy connection between female and male threaded parts. The Swivel Female x Male 90° Elbow offers a 90-degree angle for tight spaces while maintaining rotational flexibility. The Swivel Female x Swivel Female Adaptor allows for continuous rotation at both ends. The Swivel Female x Female 90° Elbow provides a 90-degree turn with a female connection at each end. Finally, the Swivel Female x Female Equal Tee allows for equal fluid flow in three directions.
Tee, Cross and Elbow Fittings
Hydraulic Tee, Cross, and Elbow Fittings are regular used components in hydraulic systems, used to manage fluid flow directions and connections. A Hydraulic Tee allows for branching fluid flow, connecting three pipes or hoses, ideal for distributing fluids to multiple areas. Hydraulic Cross fittings, with four ports, enable fluid to flow in different directions, commonly used in complex systems requiring multi-directional flow control. Hydraulic Elbow fittings, typically in 90° or 45° angles, change the direction of fluid flow in confined spaces, minimizing pipe strain. These fittings play a critical role in maintaining efficient fluid distribution and pressure control in hydraulic, oil, gas industries.


Ferrule Fittings
Ferrule fittings are widely used in industries for creating leak-proof tube connections, and they are mainly classified into single ferrule and double ferrule types. Single ferrule fittings rely on one ferrule to create a secure seal, making them simple to install and useful for a range of applications. Suitable for low-pressure applications like up to 350 bar pressure. On the other hand, double ferrule fittings provide extra reliability with two ferrules gripping the tube, offering better resistance against vibration and high-pressure conditions. Suitable for high-pressure applications 700 bar pressure. Widely utilized in high-pressure conditions, like oil and gas sector, chemical processing plants, aerospace and aviation industries.
Hydraulic Banjo Fitting
Banjo fittings are precisely manufactured components designed for compact and efficient fluid transfer in hydraulic systems. Featuring a hollow bolt and spherical union, they enable 90° fluid connections in limited spaces while maintaining high-pressure resistance. Manufactured in Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel (304/316), or Brass, these fittings ensure durability, leak-proof performance, and compatibility with hydraulic oils, brake fluids, fuels, and lubricants. Widely used in construction machinery, earthmoving equipment, material handling systems, and industrial presses, banjo fittings provide reliable sealing with copper or bonded washers.

Understanding Threads
Hydraulic fittings are Important for ensuring safe and leak-free connections in hydraulic systems, and the type of thread used plays a major role. Each thread standard (BSP, NPT, JIC, ORFS, etc.) is designed for specific pressure ratings, sealing methods, and applications. Using the correct thread ensures proper alignment, tight sealing, and resistance to vibration, preventing fluid leakage and system failure. Incorrect or mismatched threads can cause cross-threading, weak joints, or dangerous blowouts under high pressure. Therefore, selecting the right thread type in hydraulic fittings is essential for safety, efficiency, reliability, and long-term performance of hydraulic systems.
NPT Threads
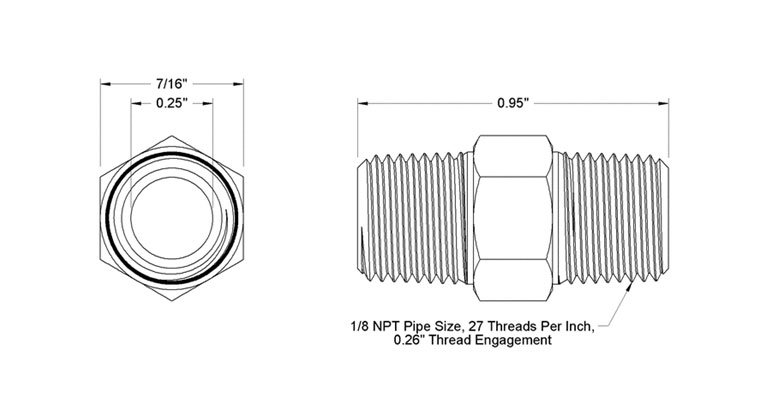
National Pipe Taper (NPT) threads are one of the most commonly used thread types in the United States, especially in the plumbing and gas fitting industries. Unlike straight threads, NPT threads are cut with a slight taper—meaning the thread diameter gradually decreases from one end to the other. This tapering design ensures that, when tightened, the threads wedge together to form a strong and reliable connection. Because of this sealing effect, NPT fittings are often the preferred choice for systems operating under pressure.
An NPT thread is defined by a 60° thread angle and a taper rate of 1 inch in 16 inches. This geometry helps achieve a snug fit that reduces the chance of leaks. Standard sizes are specified in inches, typically ranging from 1/8″ up to 6″ or larger, depending on the system’s requirements.
Where NPT Threads Are Used
Because of their strength and ability to handle pressure, NPT threads are widely applied in systems carrying liquids and gases. Typical uses in Domestic and industrial water pipelines, Natural gas distribution networks, Hydraulic equipment, Pneumatic systems etc.
BSP (BSPP and BSPT) Threads
BSPP Thread
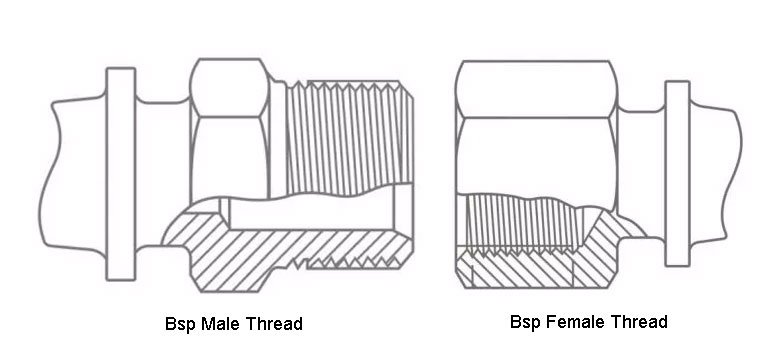
BSPP (British Standard Parallel Pipe) thread is a type of parallel thread used in the plumbing and piping industry. It is a British standard thread used for making connections in hydraulic and pneumatic systems. BSPP threads are characterized by their parallel, non-tapered form, which ensures a secure and leak-free connection when sealed with a washer or O-ring. BSPP follow the Whitworth thread system, with a 55-degree angle, and are designed for use in applications requiring a constant diameter.
Identifying BSPP threads is relatively simple. BSPP threads are parallel, which means the thread’s diameter remains consistent along the length of the fitting. They are often marked as “BSPP” on the product, indicating their specification. A key feature of BSPP is that it does not use tapered threads like BSPT (British Standard Tapered) threads. A simple comparison with BSPT threads, which feature a cone shape, will help differentiate them. Additionally, BSPP threads typically require sealing through a gasket or O-ring.
Where BSPP Threads Are Used
BSPP threads are commonly used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems, particularly for applications where pressure-tight connections are necessary. They are found in industries like automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. BSPP fittings are also commonly used in water supply systems, gas installations, and other fluid control systems due to their reliability in preventing leaks.
BSPT Thread
BSPT Thread
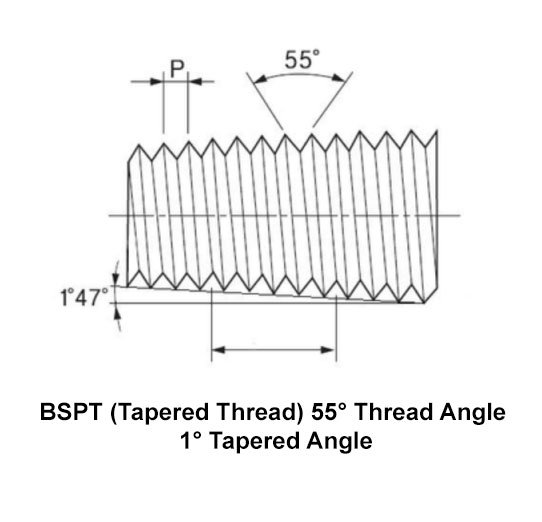
BSPT (British Standard Tapered) thread is a type of tapered thread commonly used in piping systems. Unlike BSPP threads, which are parallel, BSPT threads have a tapered design. This tapering allows for a tighter seal as the threads tighten, making it ideal for applications requiring a secure, pressure-tight connection. BSPT threads are designed to create a stronger bond when they are tightened, helping to prevent leaks.
Identifying BSPT threads is relatively straightforward. The most notable feature is their tapered shape, where the diameter of the threads decreases as they move along the length of the fitting. BSPT threads are also often marked with “BSPT” on the product for easy identification. Unlike BSPP threads, BSPT threads require thread sealing compounds or PTFE tape to ensure a leak-free connection. Visual inspection for the conical shape is an easy way to distinguish BSPT threads from other types of threads.
Where BSPT Threads Are Used
BSPT threads are widely used in industries requiring high-pressure and leak-resistant connections, such as oil, gas, and hydraulic systems. They are commonly found in applications like pipe fittings, valves, and compressors. The tapering design ensures a more reliable seal in environments where vibration and pressure changes are frequent, making BSPT threads ideal for industrial and automotive uses.
JIC Thread
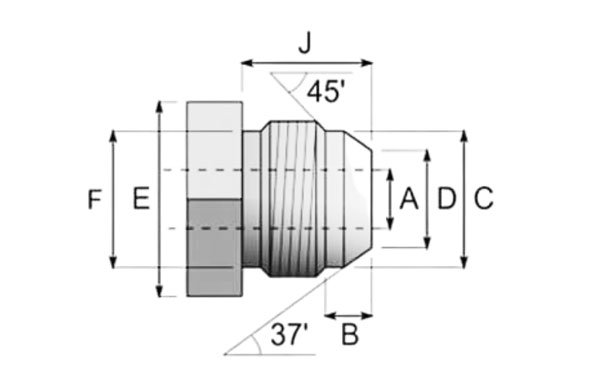
JIC (Joint Industrial Council) threads are a type of standardized threaded connection used primarily in fluid and hydraulic systems. These threads are part of the SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) standard and are normally use in industrial, automotive, and aerospace applications. JIC threads are designed to create a tight, leak-proof seal when mated with a flare fitting, where the mating surfaces form a metal-to-metal connection. This ensures a secure and reliable joint for fluid transfer. The JIC thread is characterized by a 37-degree flare angle, which is a key feature that differentiates it from other types of threads, such as NPT (National Pipe Thread). The 37-degree angle creates a larger contact area between the flare and the fitting, enhancing sealing performance under high pressure and extreme conditions.
JIC threads are commonly used in applications involving hydraulic lines, fuel lines, and refrigerant systems where high-pressure fluid transfer is required. Their robustness makes them suitable for environments with high vibration, temperature changes, or aggressive chemicals. The JIC connection’s ability to resist leakage under high-pressure conditions is one of the main reasons it is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction equipment.








